Tax season can be complex, especially if you’re utilizing a Health Savings Account (HSA). HSAs offer a triple tax advantage: contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and qualified withdrawals for medical expenses are tax-exempt. However, reporting HSA activity on your tax return requires Form 8889, Health Savings Accounts. This informative guide by Syed Professional Service dives into Form 8889, explaining its purpose, critical sections, and how our team can confidently empower you to navigate HSA tax benefits.
Understanding Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Form 8889
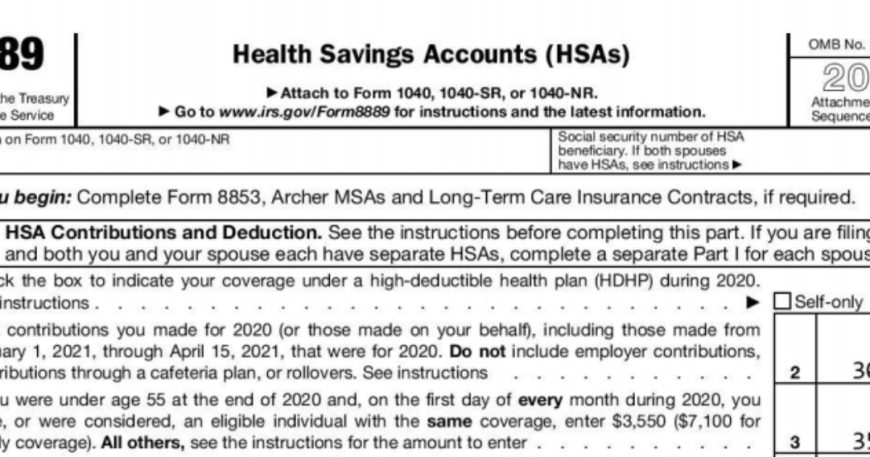
An HSA allows you to set aside money on a pre-tax basis to pay for qualified medical expenses. The funds roll over year-to-year, and unused contributions can be invested for long-term growth. However, to qualify for the triple tax advantage of HSAs, you must be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). Form 8889 is the official document for reporting your HSA contributions and distributions and calculating any related taxes on your federal tax return.
Who Needs to File Form 8889?
You are required to file Form 8889 if you meet any of the following criteria:
- Made HSA Contributions: If you contributed any money to your HSA during the tax year, you must file Form 8889, even if you didn’t withdraw.
- Took HSA Distributions: If you withdrew money from your HSA during the tax year, you must report it on this Form to determine if any portion is taxable.
- Made Non-Qualified Distributions: If you withdrew funds from your HSA for non-qualified medical expenses, you’ll owe income tax and a 20% penalty on the non-qualified amount. Form 8889 helps you calculate this tax liability.
Understanding Key Sections of Form 8889
While Form 8889 might seem complex, understanding its sections simplifies the process. Here’s a breakdown of the critical parts:
- Part I – HSA Information: This section gathers details about your HSA, including the name of the HSA provider and the account number.
- Part II – HSA Contributions: Here, you’ll report the total contributions made to your HSA for the tax year. Your HSA records or Form 5498-SA can provide you with this date every year, often delivered in January. The third part of the document, focusing on HSA distributions, reveals the total amount of funds removed from your account during the fiscal year and how much of that total went towards qualified medical expenses.
- Part III – Qualified HSA Funding Distributions: This section applies if you rolled over funds from a traditional IRA or Roth IRA to your HSA. It’s a complex process with tax implications, so consult a tax professional if you consider this option.
Maximizing Your HSA Tax Benefits: Beyond Form 8889
While Form 8889 plays a central role, here are some additional considerations for maximizing your HSA tax benefits:
- Understanding Contribution Limits: The IRS sets annual contribution limits for HSAs. Exceeding these limits can result in tax penalties. Refer to the IRS website for the latest contribution limits.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain detailed records of your HSA contributions, distributions, and qualified medical expenses throughout the year. The IRS might request this documentation to verify your tax reporting.
- Distributions for Non-Medical Expenses: Remember, withdrawals for non-qualified medical expenses are taxed as income and subject to a 20% penalty. Use HSA funds strategically for qualified medical costs to reap the full tax benefits.
Syed Professional Service: Your Partner in HSA Tax Strategies
Navigating HSA tax benefits and Form 8889 can involve complexities. Syed Professional Service can be your trusted partner throughout this process:
- HSA Eligibility Assessment: We can confirm your eligibility for HSAs based on your health insurance plan and advise on contribution strategies.
- Form 8889 Completion: Our tax professionals can guide you through completing this Form accurately and efficiently. Ensuring you claim the HSA tax benefits you deserve.
- Recordkeeping Support: We can advise on best practices for maintaining organized records of your HSA contributions, distributions, and medical expenses.
Tax Optimization Strategies: Beyond HSAs, we can explore other tax-saving opportunities related to your health and medical expenses.