Navigating the complexities of federal income Tax Bracket 2025 is essential for effective financial planning. This guide aims to demystify tax brackets, provide detailed information for the tax years 2024 and 2025, and assist you in determining your applicable tax bracket.
What Are Tax Brackets?
Tax brackets are the divisions at which tax rates change in a progressive tax system. In the United States, the federal income tax system is progressive, meaning that as your taxable income increases, so does your tax rate. This structure ensures that individuals with higher incomes pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes.
Federal Income Tax Brackets for 2024
For the tax year 2024, the federal income tax brackets are as follows:
| Tax Rate | Single Filers | Married Filing Jointly | Married Filing Separately | Head of Household |
|---|---|---|---|---|
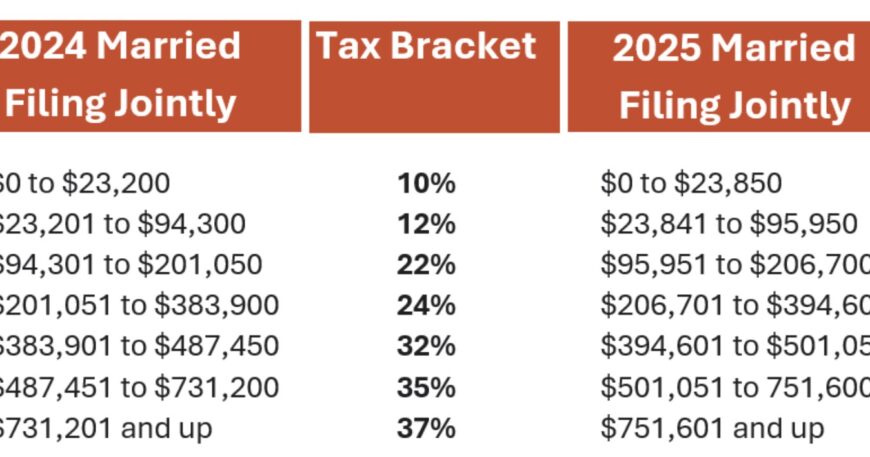
| 10% | Up to $11,600 | Up to $23,200 | Up to $11,600 | Up to $16,550 |
| 12% | $11,601 to $47,150 | $23,201 to $94,300 | $11,601 to $47,150 | $16,551 to $63,100 |
| 22% | $47,151 to $100,525 | $94,301 to $201,050 | $47,151 to $100,525 | $63,101 to $100,500 |
| 24% | $100,526 to $191,950 | $201,051 to $383,900 | $100,526 to $191,950 | $100,501 to $191,950 |
| 32% | $191,951 to $243,725 | $383,901 to $487,450 | $191,951 to $243,725 | $191,951 to $243,700 |
| 35% | $243,726 to $609,350 | $487,451 to $1,000,000 | $243,726 to $500,000 | $243,701 to $609,350 |
| 37% | Over $609,350 | Over $1,000,000 | Over $500,000 | Over $609,350 |
Source: IRS Provides Tax Inflation Adjustments for Tax Year 2024
Federal Income Tax Bracket 2025
The IRS adjusts tax brackets annually to account for inflation. For the tax year 2025, the brackets are:
| Tax Rate | Single Filers | Married Filing Jointly | Married Filing Separately | Head of Household |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | Up to $11,925 | Up to $23,850 | Up to $11,925 | Up to $16,550 |
| 12% | $11,926 to $48,475 | $23,851 to $96,950 | $11,926 to $48,475 | $16,551 to $63,100 |
| 22% | $48,476 to $103,350 | $96,951 to $206,700 | $48,476 to $103,350 | $63,101 to $100,500 |
| 24% | $103,351 to $197,300 | $206,701 to $394,600 | $103,351 to $197,300 | $100,501 to $191,950 |
| 32% | $197,301 to $250,525 | $394,601 to $501,050 | $197,301 to $250,525 | $191,951 to $243,700 |
| 35% | $250,526 to $626,350 | $501,051 to $751,600 | $250,526 to $626,350 | $243,701 to $609,350 |
| 37% | Over $626,350 | Over $751,600 | Over $626,350 | Over $609,350 |
Source: IRS Releases Tax Inflation Adjustments for Tax Year 2025
How to Determine Your Tax Bracket
To ascertain your tax bracket, follow these steps:
- Calculate Your Taxable Income: Begin with your gross income and subtract any deductions (standard or itemized) to determine your taxable income.
- Identify Your Filing Status: Determine whether you are filing as single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, or head of household.
- Locate Your Tax Bracket 2025: Using the tables above, find the range that includes your taxable income under your filing status.
For example, if you are a single filer with a taxable income of $50,000 in 2025, you fall into the 22% tax bracket.
Understanding Marginal vs. Effective Tax Rates
It’s crucial to distinguish between marginal and effective tax rates:
- Marginal Tax Rate: The rate applied to your last dollar of taxable income. In the example above, the marginal rate is 22%.
- Effective Tax Rate: The average rate you pay on your total taxable income, calculated by dividing your total tax liability by your taxable income.
Common Questions About Tax Bracket 2025
What is my Tax Bracket 2025?
YourTax Bracket 2025 depends on your taxable income and filing status. Refer to the tables above to determine where your income falls.
Do tax brackets include standard deductions?
No, tax brackets apply to taxable income, which is calculated after subtracting deductions from your gross income.
Can Tax Bracket 2025 change annually?
Yes, the IRS adjusts tax brackets annually to account for inflation and other factors.
Strategies to Manage Your Tax Budget
Understanding your Tax Bracket 2025 can help you implement strategies to manage your tax liability.
- Income Timing: If you’re close to the next tax bracket, consider deferring income to the following year to stay within a lower bracket.
- Retirement Contributions: Contributing to retirement accounts like a 401(k) or IRA can reduce your taxable income.
- Tax Credits and Deductions: Explore available tax credits and deductions to lower your taxable income.
Conclusion
Staying informed about federal income Tax Bracket 2025 is crucial for effective financial planning. By understanding where your income falls within the tax brackets for 2024 and 2025, you can make informed