The Ultimate Schedule D Handbook for the 2025 Tax Year: Everything You Ought to Know
As tax season approaches, one of the key forms taxpayers and tax professionals must be familiar with is the IRS Schedule D Tax Form. This form plays a crucial role in calculating capital gains and losses, which can significantly impact your overall tax liability. Whether you’re an individual taxpayer or a business owner, understanding when and how to file Schedule D is essential for ensuring accurate tax filings.
In this definitive guide, we will explain everything you need to know about Schedule D, including what it is, how it’s utilized, when it’s needed, and the 2024 and 2025 tax year updates. If you have ever wondered, “What is Schedule D on a tax return?” or “Do I need to file Schedule D?” Then this post is for you.
What is Schedule D? Understanding the Basics
Schedule D is a tax form used to report capital gains and losses on federal tax returns. These gains and losses generally arise from the sale or exchange of investments such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. The form helps calculate the net gain or loss, which is then reported on the main income tax return, typically Form 1040.
Schedule D is intended to help taxpayers account for capital asset gains and losses, which are taxable. If you’ve disposed of any assets during a particular year and incurred a gain or loss, you’ll most likely be required to fill out Schedule D as part of filing your taxes.
The Purpose of Schedule D on Tax Returns
The primary function of Schedule D is to assist the IRS in tracking and taxing capital gains. These gains may arise from many different types of assets, such as stocks, mutual funds, properties, and even rare collectibles like jewellery or artwork.
By using Schedule D, the IRS can identify how much income you’ve earned from the sale of assets and whether or not that income should be taxed as short-term or long-term capital gains. Here’s how it works:
Short-Term Capital Gains: These are profits from assets held for one year or less and are taxed at ordinary income tax rates.
Long-Term Capital Gains: Gains on assets owned for over one year are taxed at lower rates, generally from 0% to 20%, based on your tax status.
When is Schedule D Required?
Schedule D is necessary if you have capital losses or gains from the selling or exchanging of assets within the tax year. There are exceptions, though. Here’s how you’ll know when to file Schedule D:
When Capital Gains or Losses Arise: If you’ve disposed of stocks, bonds, real estate, or other investments, you must file Schedule D.
If You Have an IRS-Required Report of Investment Income: If you got a Form 1099-B (Proceeds From Broker and Barter Exchange Transactions), you will probably need to report the income on Schedule D.
Reporting Investment Income: Regardless of your gains being offset by losses, you still have to file Schedule D to make the proper reporting.
In brief, if you have a taxable gain or loss, either realised or unrealised, Schedule D has to be filed to comply with IRS taxation regulations.
When Is Schedule D Not Needed?
Not all taxpayers will require filing Schedule D since the form will not be needed in some situations. Here’s when you don’t have to file Schedule D:
No Capital Gains or Losses: If you did not sell or exchange any capital assets, you won’t have to file Schedule D.
Gains Are Excluded from Tax: If your capital gains are excluded from taxation under legislation such as the home sale exclusion (up to $250,000 or $500,000 for couples filing jointly), Schedule D is not required.
Non-Taxable Events: If your investment activity comprised non-taxable events, i.e., some tax-deferred transactions, you won’t be required to report those on Schedule D.
Remember to review the IRS’s specific guidelines and speak with a tax expert to verify whether you must file a form.
IRS Schedule D Instructions: A Step-by-Step Guide
Filing Schedule D can seem complex, but understanding the instructions can simplify the process. The IRS provides detailed instructions for filling out the form, which can be found on their website or included with the paper form. Here’s a basic rundown of what you’ll need to do:
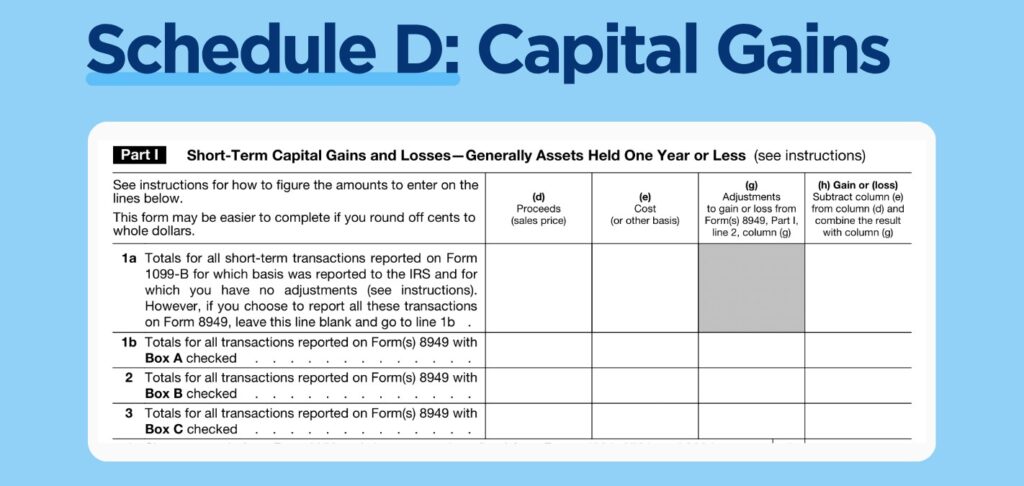
Complete Part I for One-Year or Less Short-Term Capital Gains and Losses: Report each transaction here, including sale date, amount sold, and asset cost basis.
Complete Part II for Long-Term Capital Gains and Losses. This section applies to assets held for more than a year. You’ll use the same procedure as Part I for long-term assets.
Summarise Your Total Capital Gains or Losses: After listing all your transactions, you’ll calculate the total short-term and long-term gains or losses. These totals will help determine your overall tax liability.
Transfer Information to Form 1040: Once you’ve filled out Schedule D, the final totals are transferred to your main Form 1040, either as a capital gains tax or offset against your overall income.
Complete instructions for Schedule D are available on the IRS website, or if you are unsure, contact a tax professional.
What’s New for Schedule D in 2024 and 2025?
IRS updates different forms and instructions for every tax season, and Schedule D has also been updated. Looking forward to the 2024 and 2025 tax seasons, the following are some of the significant updates one should note:
Changes to Capital Gains Tax Rates: Long-term capital gain tax rates can change based on your income level. Be sure to review the current tax bracket rules for the applicable rates.
Extra Reporting Requirements: New legislation may require more information on reportable sales of specific types, including digital assets or cryptocurrency.
Form 1040 Alignment: The IRS is constantly refining the interaction between Schedule D and Form 1040, looking out for possible revisions on filing and report structures for a more efficient process.

FAQs About Schedule D
What is Schedule D used for?
Schedule D reports short-term and long-term capital gains and losses on the sale of investments such as stocks, real estate, and bonds. It assists taxpayers in determining their total tax liability based on their net capital gain.
How is short-term capital gain different from long-term capital gain?
Short-term capital gains are from assets held for a year or less and are taxed as ordinary income. Long-term capital gains are from assets held for more than a year and are taxed at lower, preferential rates.
When do you need to file Schedule D?
You must file Schedule D if you disposed of any assets during the year that realized capital gains or losses, including stocks, bonds, or real estate.
Do I have to file Schedule D if I don’t have any capital gains?
If you had no capital gains or losses on the disposition of assets, then you do not have to file Schedule D.
Can Schedule D be e-filed?
Yes, Schedule D can be e-filed as part of your total tax return using e-filing services or tax software.
What do I do if I’m unsure I need to file Schedule D?
The best way to ensure you accurately report all your tax requirements is to talk to a tax professional or use IRS resources to review your filing needs.
Conclusion: Understanding Schedule D for a Stress-Free Tax Filing
Schedule D filing is necessary if you had capital gains or losses throughout the tax year. It enables the IRS to monitor your investment income and tax you appropriately. Knowing when Schedule D has to be filed and how to fill it out correctly can make the filing process smoother and prevent any errors.
As we transition to the 2024 and 2025 tax years, keep current on any tax law changes that might impact Schedule D and your filing situation. If you have questions or need help, don’t hesitate to contact a tax professional who can walk you through it.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes When Filing Schedule D
Schedule D filing can sometimes be daunting, particularly if there are multiple transactions to report. Even experienced taxpayers can err. To prevent common errors, I have some tips to help your Schedule D filing be as accurate as it can be:
Accurate Reporting of Cost Basis:
The most frequent error is reporting the cost basis of an asset incorrectly. Your cost basis is the price you paid for the asset plus any costs (like brokerage commissions) involved. You have a capital gain if you sell an asset for a price higher than your cost basis. On the other hand, if your sale price is less than your cost basis, you have a capital loss. Ensure that you report the cost basis accurately to avoid errors.
Check Your 1099 Forms:
You should receive a Form 1099-B from your broker if you sold any investments. This form reports the sale proceeds, and a copy goes to the IRS. Ensure that the 1099-B information matches your records. If the information does not check out, call your broker to correct it before filing.
Don’t Forget to Report All Transactions:
In case you sold more than one asset throughout the year, make sure to report all of them on Schedule D. Smaller transactions are easy to miss, but you have to report them, particularly if you received more than one 1099 form.
Look to Tax-Loss Harvesting:
If you have incurred losses on certain investments, tax-loss harvesting is something to consider to offset other gains. But do understand the “wash-sale rule,” which prevents deducting losses if you buy the same or similar securities within 30 days. Ensure you know the rules so you don’t make this error.
See a Tax Professional for Complicated Cases:
If you’ve conducted many trades or had more complicated investments like cryptocurrency, real estate, or foreign investing, seeing a tax professional is a good idea. They can walk you through the ins and outs of reporting and help ensure it’s all reported accurately to prevent audits or penalties.

The Significance of Schedule D in the 2025 Tax Year
The 2025 tax year may see alterations in treating capital gains or the taxation of new assets such as cryptocurrencies. Taxpayers must keep themselves updated on the latest news from the IRS. Here are some possible scenarios for the 2025 tax year that might necessitate changes to your Schedule D returns:
Cryptocurrency Capital Gains:
With the IRS focusing more on cryptocurrency transactions, it is important to report capital gains and losses from digital currencies accurately. Most taxpayers are unaware that cryptocurrency transactions are reportable, and omitting to report such transactions on Schedule D correctly will invite fines or penalties.
More Reporting Requirements:
While the IRS seeks greater transparency from taxpayers, there can be more reporting requirements for some investments or types of assets. For example, you might have to report more information on digital asset transactions or foreign accounts. It is essential to keep track of new IRS guidance for 2025 filings.
Tax Rate Changes:
With possible alterations in tax regulations, including higher long-term capital gains tax rates for high-income earners, Schedule D will still be essential to calculate the effect on your tax return properly. This will come into play for many taxpayers who frequently purchase and sell stocks or other investments.
Revised Form Instructions:
The IRS updates its forms periodically to keep up with new tax legislation, so the 2025 Schedule D might have new sections or varying reporting requirements. Always consult the latest IRS Schedule D instructions to make sure you’re doing things in the proper order.
How to Maximize Tax Benefits with Schedule D
While Schedule D filing is typically considered a required chore, astute taxpayers can strategically leverage it to lower their tax bill. Here are some methods through which you can optimize tax savings while filing Schedule D:
Offsetting Gains with Losses (Tax-Loss Harvesting):
If you have a year in which you have had both capital losses and gains, you can offset the gains with the losses, a technique that is referred to as tax-loss harvesting. This decreases the taxable amount of capital gains and, in certain instances, permits you to deduct up to $3,000 of overhanging losses from your regular income. This is a very useful strategy for those in higher tax brackets.
Long-Term Capital Gains Advantages:
If you’ve owned an asset for over a year, you’ll get to keep the lower long-term capital gains rate, usually less than the short-term gains rate. Timing your investment sales on this basis can save you money.
Qualified Opportunity Funds (QOFs):
If you invest in a QOF, you could qualify for favorable tax incentives, such as deferral of capital gains. Although this requires more sophisticated planning, it’s a great way to minimize taxes in the long run.
Tax Planning with Retirement Accounts:
Most taxpayers save tax-deferred in tax-favoured retirement accounts such as IRAs and 401(k)s. While you do not have to report such accounts on Schedule D, knowing their treatment in the context of capital gains can assist you in planning more effective tax savings.
Conclusion: Keep Up with Schedule D for a Trouble-Free Tax Filing
Tax returns can be confusing, but understanding when and how to report Schedule D can make the experience much smoother, especially when you have capital gains or losses. With the changes in the 2024 and 2025 tax years, monitoring whether and when the tax regulations are changing and impacting how you will report your investments is essential.
By reading the IRS instructions closely, staying clear of typical errors, and considering tax-saving strategies, you can optimise your financial condition and minimise the chances of mistakes. Regardless of whether you are preparing on your own or with the help of a tax professional, knowledge regarding the use of Schedule D is essential to make your tax return accurate and helpful.
Why Do You Always Choose Syed Professional Services?
Expertise and Experience:
Syed Professional Services is known for its deep understanding of various industries and its ability to handle complex tasks. Whether you need tax advice, financial consulting, or general business services, the team has the knowledge and experience to meet your needs.
Customer-Centric Orientation:
Syed Professional Services always offers customized solutions to every client. The staff pays close attention to your issues and strives to create strategies that are in keeping with your objectives, resulting in the most favourable outcomes.
End-to-End Services:
They offer a comprehensive list of professional services so that clients can count on them for various requirements, including tax preparation, strategic business guidance, and accounting services.
Reliable and Transparent:
Trust is important, and Syed Professional Services is known for being transparent and honest in everything it does. Clients can trust them to provide clear guidance, well-defined strategies, and transparent pricing.
Flexibility to Evolving Needs:
Whether an individual or a company, Syed Professional Services aligns with tax law changes, financial regulations, and other industry-related changes; they are always adjusting to what is happening in the market to offer clients the best possible services and advice.
What Can Syed Professional Services Do for You?
Tax Preparation and Filing:
Syed Professional Services can assist with tax planning, preparation, and filing for individuals and businesses. If you have complex forms, such as Schedule D, or are confused about deductions and exemptions, their staff ensures proper filings, which helps reduce tax liabilities.
Accounting and Bookkeeping:
Proper financial records are crucial for companies. Syed Professional Services provides professional accounting and bookkeeping services to keep your company in order, compliant, and in good financial health.
Financial Planning Consulting:
Whether planning for retirement, investing, or expanding a business, Syed Professional Services offers insightful consulting services that align your financial decisions with your long-term goals. Their experts assist you in developing personalized financial strategies and wealth-creation plans.
Business Structure and Formation Guidance:
Starting a business may be a complex process. Syed Professional Services helps business owners create their companies, guides them on the most optimal structure (LLC, corporation, etc.), and assists in understanding the associated legal and tax implications.
Audit Representation and Tax Support:
In case of an audit, Syed Professional Services offers professional representation to defend your case before the IRS with the highest level of care and professionalism.
Payroll Services:
Payroll is a labour-intensive and cumbersome function for most companies, particularly as you expand. Syed Professional Services provides payroll management services to guarantee that your employees receive timely payments and that all tax filings on payroll are done properly.
Strategic Business Consultation:
Suppose you want to enhance your firm’s financial position, increase your operations, or minimize taxes. In that case, Syed Professional Services provides strategic business consulting services to help you make informed choices that advocate for your business development.
Legal and Compliance Support:
Tax laws, business regulations, and other compliance issues can be overwhelming. Syed Professional Services can help you navigate the web of legal constraints, ensure compliance, and avoid penalties.
Essentially, Syed Professional Services is an all-in-one solution to most professional requirements, providing dependable, skilled, and personalized services to assist individuals and companies in effortlessly traversing complicated financial, tax, and regulatory environments. Whether you are a businessman looking for strategic guidance or an individual looking for professional tax guidance, Syed Professional Services offers the assistance you require to thrive.




